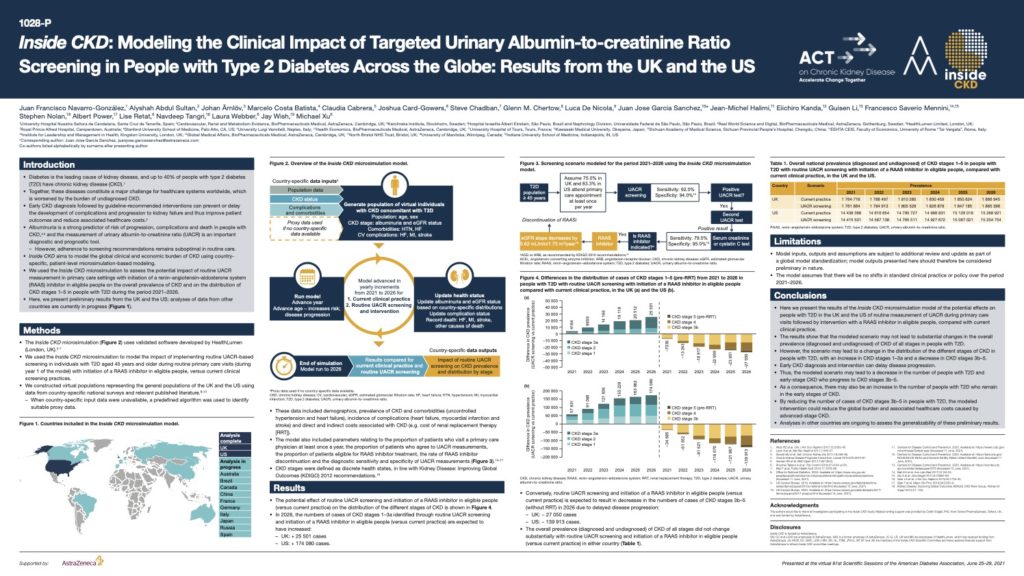
Inside CKD: Modelling the Clinical Impact of Targeted Urinary Albumin-to-creatinine Ratio Screening in People with Type 2 Diabetes Across the Globe
Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney disease, and up to 40% of people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) have chronic kidney disease (CKD) Together, these diseases constitute a major challenge for healthcare systems worldwide, which is worsened by the burden of undiagnosed CKD. Early CKD diagnosis followed by guideline-recommended interventions can prevent or delay the development of complications and progression to kidney failure and thus improve patient outcomes and reduce associated healthcare costs.
Albuminuria is a strong predictor of risk of progression, complications and death in people with CKD and the measurement of urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) is an important diagnostic and prognostic tool.
This poster, presented at the virtual American Diabetes Association’s 81st Scientific Sessions, June 25–29, 2021 demonstrates the potential effects on people with T2D in the UK and the US of routine measurement of UACR during primary care visits followed by intervention with a RAAS inhibitor in eligible people, compared with current clinical practice. By reducing the number of cases of CKD stages 3b–5 in people with T2D, the modelled intervention could reduce the global burden and associated healthcare costs caused by advanced-stage CKD.

Inside CKD: Modelling the Future Global Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is an established risk factor for CKD, and up to 40% of patients with T2D have CKD.
This poster, presented at the virtual American Diabetes Association’s 81st Scientific Sessions, June 25–29, 2021 demonstrates that from 2021 to 2026, the population of patients with CKD concomitant with T2D is projected to increase from 1.76 M to 1.87 M in the UK and from 14.4 M to 15.3 M in the US.
These projections indicate that CKD in patients with T2D will pose a substantial challenge to public health and underline the need for interventions to increase early diagnosis and delay disease progression.

The long-term health impacts of changing exposure to air pollutants in London
Transport for London (TfL) and the Greater London Authority (GLA) commissioned HealthLumen to quantify the health impacts of policies designed to reduce levels of air pollution and improve long-term health. This 2020 study estimates the number of new cases of disease and the resulting costs to the NHS and social care system under three scenarios from 2016 to 2050. The results from this study show that the ULEZ policies and broader, more all-encompassing LES policies have important impacts on the health of Londoners.

REBALANCE: Mixed-methods systematic review and economic evaluation for severe obesity
A study to systematically review bariatric surgery, weight-management programmes (WMPs) and orlistat pharmacotherapy for adults with severe obesity, and evaluate the feasibility, acceptability, clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treatment.

Obesity in primary care: Screening and brief intervention
The Brief Intervention for Weight Loss Trial enrolled consecutively attending primary care patients who were obese and participants were randomised to physicians opportunistically endorsing, offering, and facilitating a referral to a weight loss programme (support) or recommending weight loss (advice). We use a cohort simulation to predict effects on disease incidence, quality of life, and healthcare costs over 20 years.

Inequalities in smoking and obesity in Europe predicted to 2050
This study projected educational inequalities in obesity and smoking prevalence to 2050 based on past obesity and smoking trends by education level. The conclusion was that widening educational inequalities in obesity and smoking prevalence are expected in several European countries if current trends in obesity and smoking prevalence are unaltered. This will impact on inequalities in morbidity and mortality of associated diseases such as diabetes, coronary heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Forecasting Future Trends in Obesity across Europe: The Value of Improving Surveillance
This project projected the prevalence of obesity across the WHO European region and examined whether the WHO target of halting obesity at 2010 levels by 2025 is achievable. The results were that by 2025, obesity is projected to increase in 44 countries. If present trends continue, 33 of the 53 countries are projected to have an obesity prevalence of 20% or more.

High Rates of Obesity and Non-Communicable Diseases Predicted across Latin America
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular disease and stroke are a major public health concern across Latin America. We used our microsimulation model to project BMI and related disease trends to 2050. We tested the extent to which interventions that decrease body mass index (BMI) have an effect upon the number of incidence cases avoided for each disease. Without intervention obesity trends will continue to rise across much of Latin America.

Alarming predictions for obesity and non-communicable diseases in the Middle East
This study used our microsimulation model to project obesity trends and future obesity-related disease for nine countries in the Middle East. We found that high rates of overweight and obesity increased in both men and women in most countries. Obesity is a growing problem in the Middle East which requires government action on the primary prevention of obesity.

F as in Fat: How obesity threatens America’s future
In this report we modelled the long-term health impacts of obesity in each US state. The results were used as part of an annual report produced by Trust for America’s Health and sponsored by Robert Woods Johnson Foundation.